THE DETERMINATION OF MERCURY (Hg), ARSENIC (As), SELENIUM (Se), ANTIMONY (Sb) AND BISMUTH IN FOOD AND BEVERAGE SAMPLES

The consumption of food and drink is one of the main sources of exposure to toxic metals such as mercury, arsenic, antimony and bismuth. Selenium, on the other hand, is an essential nutritional element and is often added as a supplement to food for health benefits. Selenium is also an important element in animal feed to ensure livestock wellbeing.
The determination of these metals in food samples represents a significant routine workload for many contract labs and it’s important to be able to complete the work with a high degree of accuracy, precision and sensitivity.
Coupling Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) with either cold vapour generation or hydride generation has been PSA’s core competency for nearly 40 years. With the addition of analyte separation capabilities which allows for speciation studies, PSA offers powerful analytical tools to help contract laboratories, food & feed producers and regulators alike with these determinations. Food security has never been more important.
AFS Food & Beverage ApplicationsP S Analytical offer a wide variety of application notes for these sample matrices; |
||
|
|
 |
AFS Laboratory Analysers
|
Millennium Merlin & Millennium Excalibur. The employment of PS Analytical instruments, the Millennium Merlin (MM for Hg) and the Millennium Excalibur (ME for As and the other hydride elements) that employ AFS, offer an extremely sensitive and accurate determination of these elements. Key User Benefits
|
|
Millennium Excalibur (ME) (10.055 Total As, Se, Sb, Bi & Te)
|
The automated Millennium Excalibur with its built-in hydride generation manifold & boosted hollow cathode lamp is the ideal analyser for all food sample matrices. This system is typically used to determine total As, Se, Sb, Bi and Te from a range of sample types.
|
AFS Speciation Studies |
Metal transport and toxicological properties of these elements critically depend on the form (species) in which they occur in the sample. As a consequence, trace element speciation, particularly for toxic trace elements, is nowadays considered of major importance to ensure food safety. Topical examples include:
|
There are several approaches that may be taken to effectively prepare and then analyse the fish and shellfish samples including selective analyte extraction and/or species separation using chromatographic means (both GC and LC) To increase the range of applications including speciation studies we employ a configurable chromatographic front end; theModular Interface, which is equipped with LC pump, injection valve, UV cracker, heater and cooling modules. This simple interface couples directly to the Millennium Merlin or Excalibur for seamless speciation determinations. |
|
Gas ChromatographyAnother option is to use capillary GC-AFS for mercury speciation analysis. The system comprises an atomic fluorescence spectrometer with integrated pyrolysis control unit coupled to gas chromatographic column output for the determination of mercury at ultra-trace levels. The system is suitable for both routine and research applications. Absolute detection limits of 0.2 pg are easily achieved for methylmercury and ethylmercury in a variety of food samples. |
|
|
Speciation ApplicationsA few examples of our speciation application notes for these sample matrices are given below. |
|
 |
Mercury and Methylmercury
|
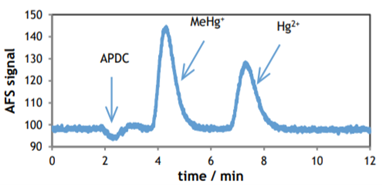 |
|||||||||||||||
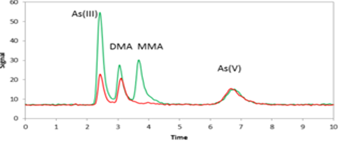
Arsenic Speciation
|
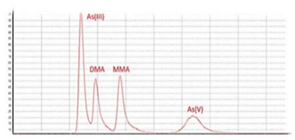
Arsenic Speciation
 |
|||||||||||||||
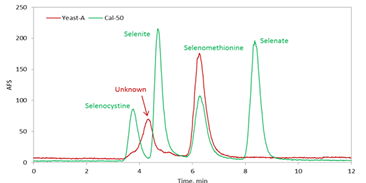
Selenium Speciation
|
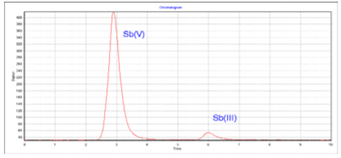
Antimony Speciation
|
|||||||||||||||
HPLC-ICP-MS v HPLC- HG-AFSThe coupling of the ICP-MS with HPLC has a number of negative consequences for a busy laboratory:
These issues are not experienced with the PSA approach. To discuss particular requirements and for more detailed information on the above products, please complete the Information Request Form. |
||||||||||||||||