ARSENIC SPECIATION
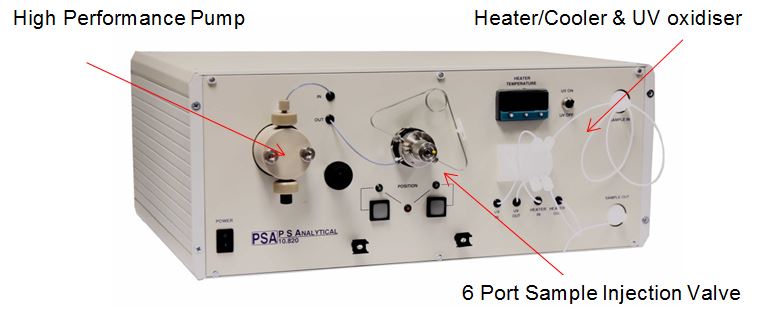
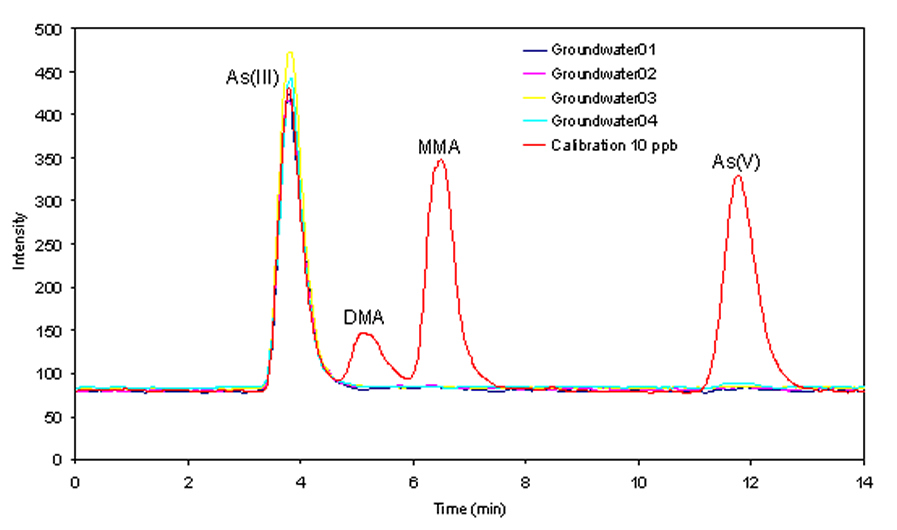
Arsenic and its compounds are known to have adverse health effects on humans, including cancers of the skin, bladder, kidney & lung, and diseases of the blood vessels of the legs and feet. The toxicity of arsenic depends very heavily on the two main chemical forms, inorganic arsenic and organic arsenic. Inorganic arsenic species (arsenite, arsenate) in ground water have caused tremendous epidemic poisoning across the globe. Organic arsenic species (typically MMA, DMA) are common metabolites found in the human body and are much less toxic. Some other arsenic forms which are very commonly presented and account for the majority of the arsenic abundance in the marine environment (arsenobetaine, arsenocholine, arsenosugars etc), are completely non-toxic. The total concentration of arsenic cannot be used solely to explain the toxicity of arsenic in the environment. As well as it's own 10.820 Modular Interface, P S Analytical offer both Agilent and Dionex options for the separation of arsenic species using the PSA 10.055 Millennium Excalibur as the detector. PSA 10.820 MODULAR INTERFACE COUPLED WITH THE 10.055 MILLENNIUM EXCALIBUR FOR THE SPECIATION OF ARSENICUp to four arsenic species; arsenite (AsIII), dimethylarsinic acid (DMA), monomethylarsonic acid (MMA) and arsenate (AsV) can be separated on a simple system. For the determination of non-reducible arsenic species such as arsenobetaine (AsB), arsenocholine and Trimethylarsine oxide ((TMAO) and arsenosugars; a PSA 10.570 UV oxidation system can be included. |
||
 |
The MI extends the capability of P S Analytical's Millennium Merlin and Excalibur Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometers and is available in a number of configurations. The MI 10.820-1000 includes:
|
|
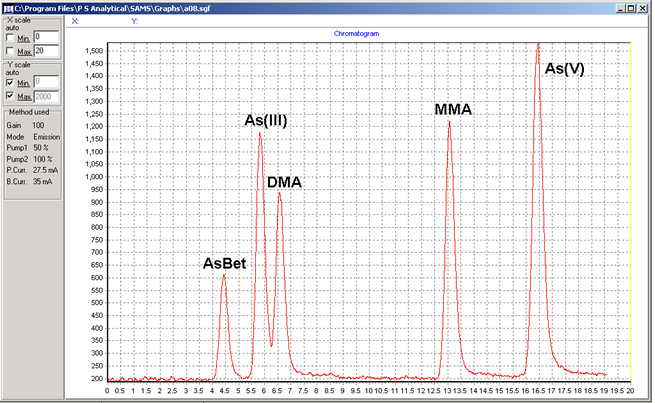
Determination of five arsenic species, arsenobetaine (AsBet), arsenite (AsIII), dimethylarsinic acid (DMA), monomethlyarsonic acid MMA and arsenate (AsV) was achieved by commercially available high performance liquid chromatography coupled to hydride generation and atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HPLC-HG-AFS). Arsenic containing human urine samples was filtered before being injected into a C18 column (PSA C2 or equivalent). Five arsenic species were separated using a phosphate mobile phase. The eluted species were converted to volatile arsines by the addition of hydrochloric acid and sodium borohydride solutions. The volatile arsines were separated from the liquid phase using a gas-liquid separator and measured as arsenic using atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Excess hydrogen from the reaction of reagents provided the hydrogen diffusion flame which atomised the arsenic species. The speciation of arsenic species including the non-reducible arsenic species (arsenobetaine and arsenosugars) requires the use of UV oxidation system. This, in conjunction with an oxidising reagent, helps the breakdown of non-reducible arsenic species to a form that will react with NaBH4 so these can be quantified. As a result, a slight modification to the system is necessary. Naturally occuring inorganic and organic As species
To discuss particular requirements and for more detailed information on the above products please complete the Information Request Form. For information on the speciation of Mercury, Selenium and Antimony please follow the appropriate link below: |